Shipping has a profound historical significance as it evolved to become the backbone of international trade. From the earliest days of human civilization, waterways, and seas were the highways that connected distant regions and civilizations. The development of seafaring technology and the establishing of trade routes allowed for the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas across the world.
Ancient maritime routes like the Silk Road and the Mediterranean trade routes facilitated the exchange of silk, spices, precious metals, and knowledge, contributing to the rise and fall of empires. As centuries passed, the shipping industry played a crucial role in the Age of Exploration, enabling the European colonial expansion and the discovery of the New World. Today, shipping remains an essential part of global trade, connecting economies, fostering globalization, and ensuring the flow of goods that sustains modern life. Its historical significance as a catalyst for global interconnectedness cannot be overstated.
Today, the global shipping industry serves as the backbone of international trade, responsible for the transportation of more than 80% of the world’s goods. In order to guarantee the secure and effective functioning of vessels while also tackling pressing environmental and safety issues, an intricate network of international regulations has been meticulously put in place. In this article, we will delve into the impact of these international regulations on the shipping industry, shedding light on their significance and the hurdles they present.
In this blog, we will cover a summary of the most tangible regulations that the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has put forward for uniform implementation. Discover how these safety, environmental, and security regulations are not just red tape but essential safeguards for maritime commerce and the environment.
The Maritime Regulatory Landscape
In the complex world of maritime regulations, a diverse array of international conventions and organizations plays a pivotal role. At the forefront of this regulatory landscape stands the International Maritime Organization (IMO), a specialized agency operating under the United Nations’ auspices, dedicated to the regulation of the international shipping industry. The IMO takes the lead in establishing and enforcing global standards for ship safety, security, and environmental protection. Explore how the IMO’s directives impact the shipping industry and contribute to safer, more environmentally responsible maritime practices.
Safety Regulations
1. SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea): SOLAS, the Safety of Life at Sea convention, is a linchpin of maritime safety standards. It meticulously prescribes the essential requirements for ship construction, equipment, and operational procedures. These guidelines encompass vital aspects such as life-saving apparatus, fire safety systems, navigation protocols, and communication methods. Compliance with SOLAS is not a choice but an unequivocal obligation for all vessels. It reflects the industry’s resolute commitment to prioritize human safety while navigating the unpredictable waters of the open sea.
2. MARPOL (International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships): The MARPOL convention exemplifies the maritime sector’s dedication to environmental responsibility. Addressing a spectrum of pollution concerns, including oil spills, noxious liquid substances, sewage discharges, and garbage disposal, MARPOL imposes stringent regulations. It compels ships to adopt pollution prevention equipment such as oil-water separators and advanced sewage treatment systems, minimizing the ecological impact of maritime activities. Furthermore, it underscores the need for environmentally responsible waste disposal practices, reinforcing the industry’s pledge to protect our oceans and safeguard their pristine condition for future generations. Explore how SOLAS and MARPOL are pivotal in ensuring maritime safety and environmental preservation.
Environmental Regulations
1. IMO’s EEDI (Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index) and SEEMP (Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan): In an era where environmental sustainability is of paramount importance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has introduced the EEDI and SEEMP regulations, which stand as beacons of change within the maritime industry. These regulations are expressly designed to combat climate change by focusing on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from ships. Under the EEDI, ships are required to meet energy efficiency standards that are set according to their size and type. This mandates the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, such as advanced propulsion systems and improved hull designs, ensuring that ships operate with greater fuel efficiency.
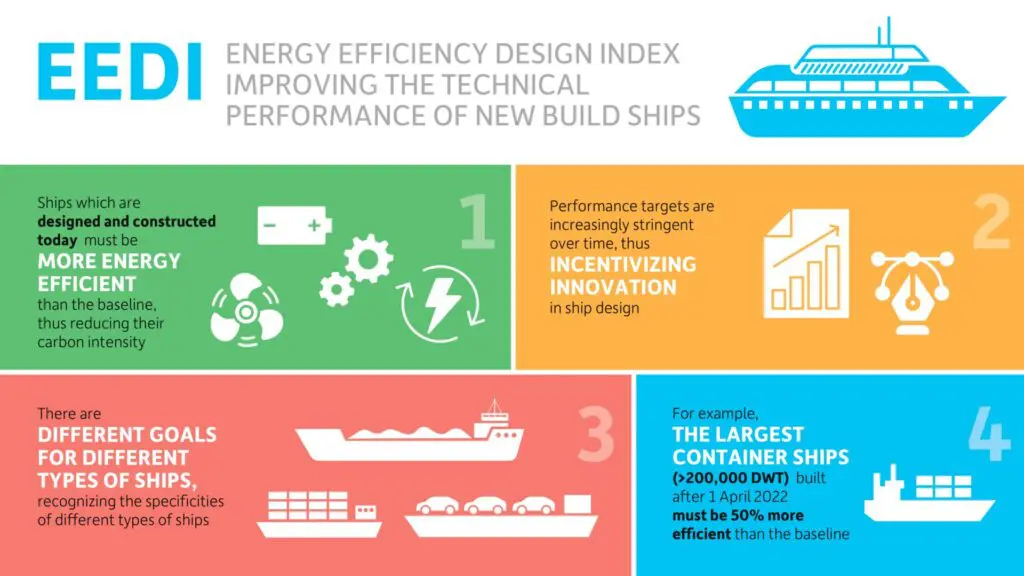
The SEEMP, on the other hand, complements the EEDI by providing ship operators with a comprehensive plan for managing and enhancing the energy efficiency of their vessels. It calls for the implementation of best practices, from optimized voyage planning to reduced engine idling times. Together, these regulations herald a new era of responsible maritime operation, with a primary focus on mitigating the industry’s environmental impact. They not only drive innovation in ship design and operation but also contribute to a greener, more sustainable future for global shipping.
2. Ballast Water Management Convention: In an interconnected world, the Ballast Water Management Convention stands as a safeguard against the inadvertent spread of invasive species. The convention addresses a critical yet often overlooked aspect of shipping: ballast water. Ships, in their quest for stability and safety, take on ballast water in one location and discharge it in another. However, this seemingly innocuous practice can inadvertently transport harmful invasive species from one ecosystem to another, causing ecological disruptions.
To counter this threat, the convention establishes rigorous standards for the treatment and discharge of ballast water. Vessels are required to install ballast water treatment systems, ensuring that discharged water meets strict environmental criteria. By doing so, the convention plays a pivotal role in preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, safeguarding biodiversity, and minimizing the unintended consequences of global trade. It’s a testament to the maritime industry’s commitment to responsible environmental stewardship, ensuring that vessels navigate the world’s waters while minimizing their ecological footprint.
Security Regulations
ISPS Code (International Ship and Port Facility Security Code): The ISPS Code represents a pivotal development in the maritime world, formulated as a direct response to the ever-pressing global security threats. This code serves as a comprehensive blueprint for bolstering security measures within the maritime domain, both aboard ships and at port facilities, with the primary objective of safeguarding against acts of terrorism.
In an era marked by heightened security concerns, the ISPS Code mandates rigorous security protocols for ships and port facilities. Vessels must implement security plans, appoint designated security officers, and conduct thorough security assessments to ensure that potential vulnerabilities are identified and addressed. Similarly, port facilities are required to put in place security measures, access controls, and surveillance systems to mitigate the risk of security breaches.
The ISPS Code is not just an instrument of safety; it is an emblem of the maritime industry’s unwavering commitment to global security. By diligently adhering to its directives, the industry strives to fortify its defenses against acts of terrorism, thereby ensuring the uninterrupted flow of international trade and the protection of precious lives and assets on the world’s seas.
Challenges and Impact on the Shipping Industry
While international regulations undoubtedly play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of crews, protecting the environment, and maintaining the security of shipping operations, they also bring forth a set of challenges that reverberate throughout the industry. These challenges are a testament to the delicate balance that must be struck between adhering to these essential guidelines and managing the operational and financial realities of the maritime sector.
1. Compliance Costs: The foremost challenge that looms over shipowners and operators is the considerable financial burden associated with compliance. Meeting the stringent requirements of international regulations often necessitates substantial investments in modern, compliant technology and equipment. From retrofitting vessels with eco-friendly propulsion systems to adopting cutting-edge pollution prevention measures, these financial commitments are substantial and can significantly impact a company’s bottom line. The imperative for compliance can translate into large upfront costs, making it a critical challenge for many industry stakeholders.
2. Administrative Burden: Navigating the sea of paperwork and administrative tasks tied to compliance is a formidable challenge. Ship operators find themselves entangled in a web of documentation and reporting requirements. Records must be meticulously maintained, and regular reports submitted to the relevant authorities. This administrative burden can be particularly overwhelming for smaller companies or those with limited administrative resources, diverting time and energy away from core operational activities.
3. Risk of Non-Compliance: Non-compliance with international regulations is a daunting prospect, as it carries a range of consequences that can severely impact a company’s operations. Penalties, detention of vessels, and damage to a company’s reputation are all potential outcomes of failing to meet the prescribed standards. The risk of non-compliance necessitates constant vigilance and a significant investment in ensuring that every aspect of a ship’s operation remains in line with these regulations.
4. Competitive Disadvantage: A unique challenge emerges when companies that diligently invest in eco-friendly technologies and adhere to safety regulations find themselves facing higher operating costs. The pursuit of compliance can lead to increased operational expenses, including fuel costs, maintenance, and the employment of additional safety personnel. These higher costs may erode a company’s competitive edge, potentially affecting its ability to remain competitive in a market where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Striking a balance between environmental responsibility and profitability becomes an ongoing challenge for the industry.
While international regulations are undeniably crucial for ensuring the responsible and safe operation of the shipping industry, they also introduce significant hurdles that necessitate careful planning and resource allocation. The sector’s ability to navigate these challenges while remaining compliant is a testament to its adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving global standards.
International regulations stand as the bedrock of the global shipping industry, serving as the ultimate guardians of safety, security, and environmental sustainability. Though they undeniably present challenges and demands for shipowners and operators, their significance cannot be overstated. These regulations are the linchpin that ensures the well-being of crews, the protection of our precious oceans, and the overall integrity of international trade.
The maritime sector, as a vital cog in the machinery of global commerce, must recognize that adherence to these regulations is not a choice but an imperative. In doing so, it not only safeguards the lives of those who brave the world’s seas but also secures the delicate ecosystems that define our planet. The shipping industry, in its perpetual quest for progress, must embrace change and continue to invest in compliance, adapting to the evolving standards set forth by international regulations.
As we move forward, it is paramount to acknowledge that these regulations are not adversaries but essential allies. They serve as guiding stars, steering the industry toward a safer, more secure, and environmentally responsible future. The ability of the shipping sector to meet these challenges head-on is a testament to its resilience and commitment to a better tomorrow. By doing so, the industry paves the way for a maritime world that thrives while minimizing its impact on the environment, ensuring that international trade remains a force for global prosperity and well-being.
Stay tuned as we bring you more in-depth news on the shipping industry and how this impacts recruitment in our next blog post.





[…] our previous blog post, we established that the shipping industry is the “lifeblood of global trade” and how a […]